What Is Horse Decoration Called
The western saddle is a marvelous cosmos. It is designed specifically for western riding. Referred to by some as a 'cowboy' saddle, the western saddle is oftentimes seen on ranches and farms, especially – but not exclusively – in North America.
The western saddle was originally designed to withstand long trail rides, ranch work, and rough treatment. When you await at the combination of class and office, you can run across that the western saddle is truly a work of fine art. Many western saddles even have intricate artwork and decoration to stand out in competitions.

The design of a western saddle is very complex. Every role of the western saddle serves a purpose and is extremely of import to its employ. All equestrians should know the different parts of a saddle, understand what their purpose is, and know how to determine what design and size of saddle they need to ride their horse efficiently.
The information provided here will help you learn more about each role of the western saddle and its purpose.
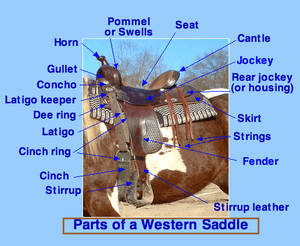
TREE
The kickoff of each saddle starts with the tree. The tree is considered to be the "skeleton" of a saddle and every subsequent part of the saddle is designed co-ordinate to the design of the tree.
The majority of western saddle copse are created using wood wrapped with rawhide, but some are covered in fiberglass instead of rawhide. The trees of saddles differ according to what kind of western saddle is being designed.
What's common to all saddles though is that the tree should be designed professionally and using quality materials, since information technology volition serve as the base for the rest of the saddle. (source)
GULLET
This is the tunnel created underneath the saddle when it sits on top of a horse'south withers. The gullet must be formed just correct so that it fits the size and shape of the horse that volition be wearing it. If it is the wrong fit, it will cause discomfort to the horse.
When the saddle sits on the equus caballus, there should be a tunnel that forms below the swell and the peak of the gullet to a higher place the withers should be somewhere effectually the width of 2 to 4 fingers. (source)
HORN
Every western saddle has a horn, making information technology one of the primal ways to distinguish western saddles from English ones. The horn is at the front of the saddle and sits on meridian of the dandy, also known as the pommel or fork.
The horn serves a few purposes, including stabilizing the passenger when getting on or off the equus caballus. Information technology as well provides a place for the passenger to attach a rope when roping a cow or other animal.
The horn comes in a variety of sizes depending on the purpose of the saddle and the comfort of the rider. For example, roping saddles tend to have a larger horn to support a rope and other accessories. Barrel racing saddles tend to accept smaller horns that slant forward because the riders volition lean forward and often concur the horn for support.
The horn is also an excellent tool for beginner riders to help them experience safe and secure int he saddle!

SWELL, POMMEL, AND FORK
The peachy, as well chosen the pommel or the fork, is the part of the saddle that sits on the front of the saddle at the base of the horn. It connects the bars (the 2 sides of the tree) of the saddle and provides a level of protection when riding.
The cracking helps proceed the rider in the saddle if they are thrown frontward and information technology gives them something else to grab onto in scary situations. The groovy also helps when moving a saddle or putting it on a horse. Riders volition grab the swell and the back of the saddle to lift it on the horse. (source)
SEAT
The seat sits behind the horn and is the place where the rider will sit when riding a horse. The seat is positioned right on height of the saddle'south tree.
The size and slope of the seat on a western saddle volition make up one's mind the condolement level for each rider. There are 3 different slopes including a high slope, a medium slope and a depression slope. The most comfortable saddle seats take a curved ground seat that serves as the base and helps make them more comfortable than flat seats.
The seat is finished past adding layers of materials that improve comfort for riders while also keeping them close to the horse. The finished seat can be difficult or soft, and both styles tin be comfortable if the seat itself was designed properly. (source)

CANTLE
The cantle is the back role of the saddle that extends out from the seat. Information technology serves as the dorsum portion of the saddle seat and provides additional support to the rider. It tin can be college or lower depending on the blueprint of the saddle and its purpose.
The cantle, like the bully, helps to continue the passenger in the saddle. Some riders apply the cantle to stabilize themselves when riding. The cantle also stabilizes the bars at the back, like the swell does at the front end. (source)
Skirt
The skirt of the saddle is the large piece of leather or other textile – depending on the saddle – that sits underneath the seat of the saddle.
Information technology is a blazon of barrier that typically has sheepskin or another cushioning material that protects the horse and helps to keep the equus caballus pads in place. The skirt also helps to balance the saddle past distributing the weight evenly.
RIGGING
The rigging is comprised of a few essential pieces that attach the saddle to the horse – the sure-fire, two D-rings, the latigo and the off-billet strap.
The cinch, also known as the girth, secures the saddle to the horse and is positioned towards the front end of the saddle. The off-billet strap connects the cinch to the D-band of the saddle on ane side while the latigo attaches the cinch on the other side of the saddle through the D-band on that side.
The rigging is a central component to all saddles and needs to exist continued correctly to the saddle to prevent accidents. (source)
LATIGO KEEPER/Tie STRAP
The latigo keeper, also called the tie strap, sits towards the forepart of the saddle near the dandy or pommel. It has an opening where the rider can place the slack from the latigo after tightening the rigging to the horse. It keeps the latigo terminate from possibly getting hung upwards or hit the equus caballus when riding.

REAR/Dorsum Sure-fire
The rear sure-fire, also called the back sure-fire, sits towards the back of some western saddles and provides additional security for the saddle. It keeps the back portion of the saddle from lifting when riding and this helps to reduce some of the pressure level the saddle puts on a horse.
The rear cinch is meant to be snug, simply not loose or overly tightened. Not every passenger using a western saddle uses a rear cinch, only if they do, they should always connect information technology to the girth/front cinch using a hobble, a leather strip that has a clasp on each stop. The rear cinch is connected to the saddle on each side by a billet. (source)
SEAT JOCKEY
The seat jockeys, also called the housing, on a western saddle are pieces of leather that flair out from each side of the seat as well as at the rear.
The jockeys serve to protect the rigging from the legs and vesture of the rider and it provides a barrier to protect exposed portions of the saddle tree. The d-ring that the cinch connects to sits partially under the jockey, which keeps it from getting hung upwardly on the rider'south legs.
FENDER
At that place is a pair of fenders on each western saddle. The fenders sit on each side of the saddle and are where the passenger'southward legs residuum when mounted.
The fenders go on the rider's legs from straight touching the horse and the come in three different shapes known every bit the Phoenix, the Arizona and the pear. The fender tin be adapted to fit the length of the passenger's legs. The fenders on a western saddle are permanently attached. (source)
STIRRUP
A stirrup is fastened to the terminate of each fender. This is where the rider's feet will go while they are riding.
The stirrups on a western saddle play a huge role in the rider'southward condom, stability, and residuum. They allow the rider to mountain the horse easily and they provide added back up when they ride the equus caballus.
Stirrups, forth with the fender, are designed in a way to proceed the rider's kicking from getting hung up in the stirrup if they were to fall off the horse. Stirrups can exist basic or oversized, depending on the size of boot the rider wears. (source)
BREASTPLATE/BREAST COLLAR
The breastplate, also called the chest neckband, is ofttimes purchased separately from the saddle, but it is an integral part of the western saddle and serves a valuable purpose.
The breastplate attaches to each side of the front of the saddle and wraps around the chest of the horse. It helps to keep the saddle from sliding backwards or from side to side every bit the horse is being ridden. The breastplate also provides boosted security to the saddle, preventing it from sliding under the equus caballus if the cinch breaks loose. (source)

Final Thoughts
The western saddle is complex and non merely provides comfort for the rider, but also added stability and security. All of the individual parts come together to class a rubber, dependable and visually appealing saddle that can concluding a lifetime.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:WesternSaddleParts.png
You have Successfully Subscribed!
Source: https://www.helpfulhorsehints.com/western-saddle-parts/
Posted by: alvaradoshle1989.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is Horse Decoration Called"
Post a Comment